
- Funded by: Croatian Science Foundation
- Call identifier: IP-2024-05-6868
- Acronim: STACOBEAM
- Duration: 16 Dec. 2024 – 15 Dec. 2027
- Principal investigator: Prof. Goran Turkalj, Ph.D.
- Project members:
- Prof. Domagoj Lanc, Ph.D.
- Assoc. Prof. Goranka Štimac Rončević, Ph.D.
- Postdoc. Damjan Banić, Ph.D.
- Postdoc. Sandra Kvaternik Simonetti, Ph.D.
- Assist. Raul Ivan Gašljević (HRZZ doktorand)
- Abstract:
Since contemporary load-carrying structures usually contain slender beam structural elements, usually with a thin-walled cross-section, the response of such weight-optimized structures to the action of external loads is at the same time much more complex, and their increased tendency to instability of deformation forms and the buckling failure is particularly pronounced. Instability of beam members could occur in a pure flexural, pure torsional, torsional-flexural or lateral deformation form, respectively. Each of them belongs to so called global buckling forms. At thin-walled beam members a local buckling form can occur, in which a cross-section deforms significantly, causing the member collapse before the occurrence of some of the global buckling forms.
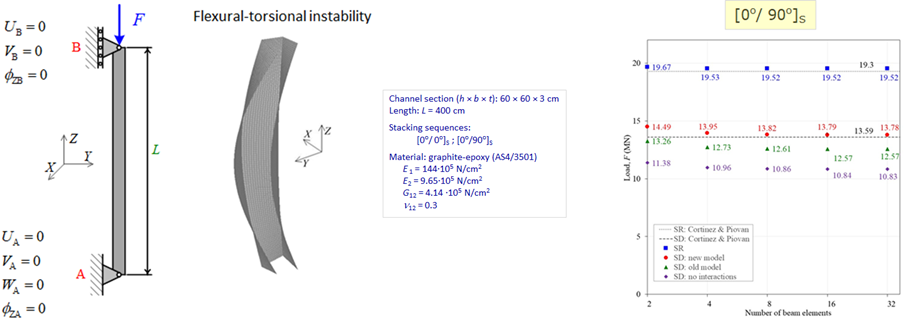
Furthermore, interest of researchers for various types of composite structures has been growing rapidly in the last few decades. The great potential of laminate, FRP (fiber reinforced polymers) and FG (functionally graded) composites causes the frequent replacement of conventional materials in engineering applications, primary in aerospace industry and in past few decades also in civil engineering applications, due to the various advantages, primarily their durability, lightness and corrosion resistance, wherever is possible and cost-effective. Thus, in the optimal structural design an important consideration should concern the accurate prediction of the stability limit state of possible deformation forms, i.e. the buckling strength.
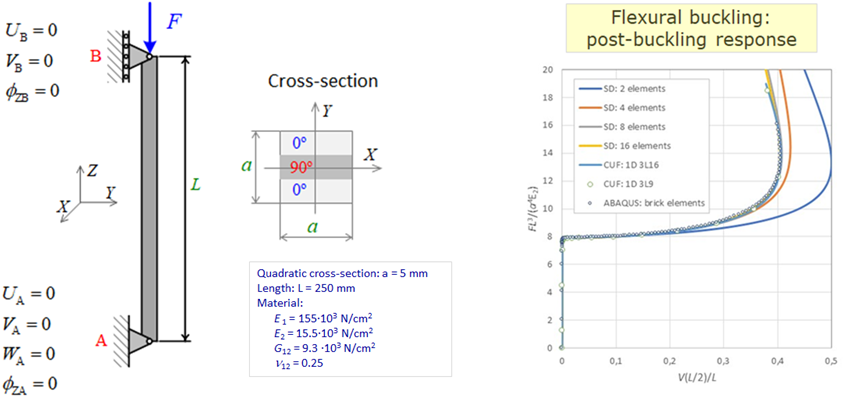
While analytical solutions are available for simpler cases, the need for numerical solutions arises in more complex scenarios. To address these challenges, researchers have introduced geometric nonlinear analyses of composite beam structures considering large rotation effects, cross-sectional warping and shear deformation effects, respectively, thermal effects. Some studies also incorporate bending-torsion coupling effects occurring when the principal bending and shear axes of a cross-section do not coincide, or due to the nonsymmetric and unbalanced stacking sequence at laminates.
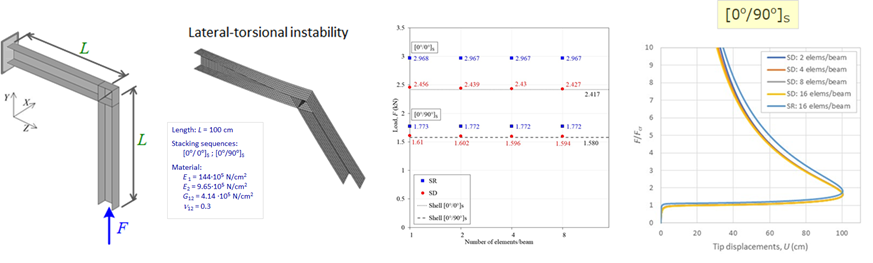
The project will deal with the further development of the existing numerical model, previously developed by the project memebers, for stability analyzing of thin-walled beam and frame structures composed of unbalanced and asymmetrical laminate composites, and of FG (functionally graded) composites under regimes of variable temperature and moisture. Numerical algorithms will be based on a spatial thin-walled beam finite element with 14 degrees of freedom of motion. As a strain measure, the Green-Lagrange strain tensor will be used, obtained on the basis of the nonlinear displacement field of the composite thin-walled cross-section, which includes the effects of large spatial rotations an warping. To obtain the equilibrium equations of the spatial beam finite element, the principle of virtual works and the updated Lagrangian incremental description will be applied. In the nonlinear stability analysis, incremental-iterative procedures for solving the nonlinear system of algebraic equations will be used. To perform the force recovery procedure, a transformation matrix based on semi-tangential rotations will be used, which are energetically conjugated with semi-tangential moments and have the property of commutativity.
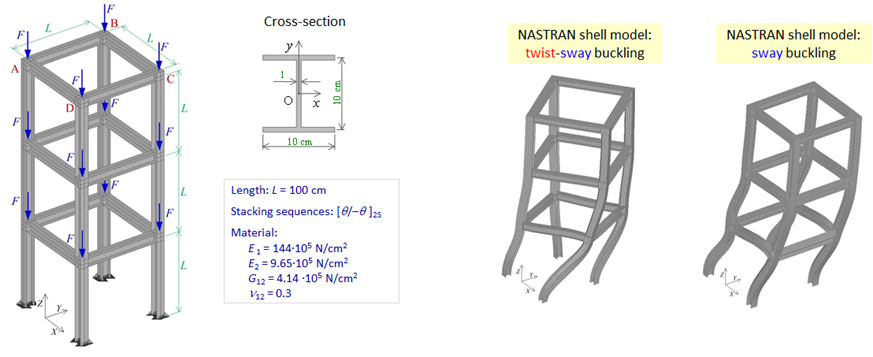
- Publications:
- Kvaternik Simonetti, S.; Lanc, D.; Turkalj, G.: Thermal stabilityanalysis of FG composite beam-type structures with open thin-walled cross-section considering temperature distributions, Composite Structures, 371, 2025, 119503, doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2025.119503.
- Štimac Rončević, G.; Skoblar, A.; Braut, S.; Žigulić, R.: Application of reciprocal condition number in vibration analysis, Journal of Sound and Vibration, 618, 2025, 119342, doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2025.119342.
- Turkalj, G.; Banić, D.; Lanc, D.: A Finite Element Formulation for buckling Analysis of unbalanced laminated beam-type structures, in P. Iványi, J. Kruis, B.H.V. Topping, (Editors), Proceedings of the Eighteenth International Conference on Civil, Structural and Environmental Engineering Computing, Civil-Comp Press, Edinburgh, UK, Online volume: CCC 10, Paper 14.1, 2025, doi:10.4203/ccc.10.14.1.
- Kvaternik Simonetti, S.; Lanc, D.; Turkalj, G.: Thermal buckling analysis of FG porous thin-walled beam, in P. Iványi, J. Kruis, B.H.V. Topping, (Editors), Proceedings of the Eighteenth International Conference on Civil, Structural and Environmental Engineering Computing, Civil-Comp Press, Edinburgh, UK, Online volume: CCC 10, Paper 14.1, 2025, doi:10.4203/ccc.10.14.1.
- Štimac Rončević, G.; Skoblar, A.; Braut, S.; Žigulić, R.; Turkalj, G.: Regression-based machine learning for predicting natural frequencies of thin beams supported by translational springs, 11th International Congress of Croatian Society of Mechanics: Book of Abstracts, Čanađija, M.; Škec, L. (Eds.). Zagreb: Croatian Society of Mechanics, 2025. pp. 179-180.
- Kvaternik Simonetti, S.; Lanc, D.; Turkalj, G.; Banić, D.: Buckling analysis of FG porous thin-walled beams under thermo-mechanical load, 10th International Conference on Mechanics of Composites: Book Of Abstracts, António Joaquim Mendes Ferreira (Ed.), Porto, Portugal, 2025.